@smoge
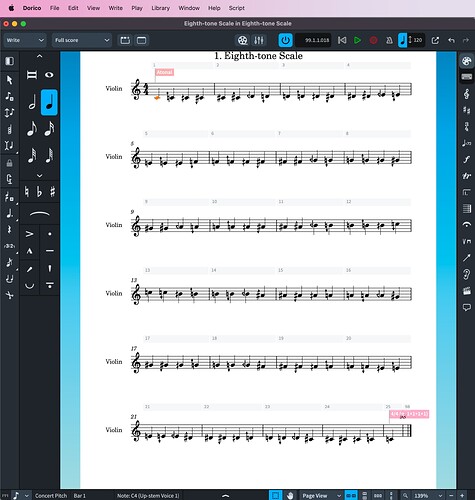
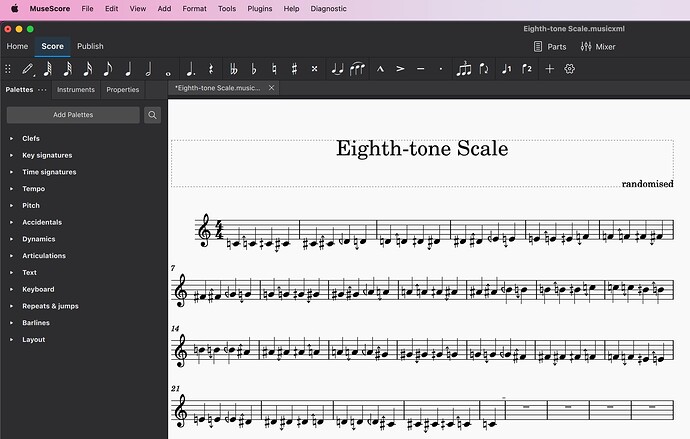
I added eighth-tone accidentals. My system is not any standard accidental system categorised in a particular one in SMuFL. E.g.: Gould arrow quartertone accidentals (24-EDO) · Standard Music Font Layout
It is still a function based on the following post.
This time the Lilypond pitch notation is supported. Below is the revised function:
Below is an example of the code to generate eighth-tone scales:
(
var title = "Eighth-tone Scale";
~score6 = [
(title: title, composer: 'randomised', right: '©'),
(
bar: 1,
p1: (
lbl: 'Violin',
atr: (key: [0, \none], time: [4, 4], staves: 1, clef: [[\g, 2]])
)
)
];
(0, 1/4 .. 12).mirror.do { |sixteenth, i|
var bar = (i / 4).floor + 1;
~score6 = ~score6.add((bar: bar, p1: (v1: [])));
~score6[bar][\p1][\v1] = ~score6[bar][\p1][\v1].add([sixteenth + 60]) // correct! thanks @smoge
// ~score6[bar][\p1][\v1] = ~score6[bar][\p1][\v1].add(sixteenth + 60) // incorrect!
};
~exportXML.(~score6, ("~/Downloads" +/+ title ++".musicxml").standardizePath, 'MuseScore 4');
)
Dorico does not indicate ‘double-sharp-down’. I think this is OK, because I think ‘c with double-sharp-down’ should be notated as ‘d with natural-down’. So my new function will do this automatically when entering pitches by MIDI note pitch numbers, as in the example code above. Please let me know if these notations are acceptable. If not, I could change it, or write a subfunction to decide the enharmonic spelling by looking at the next pitch.
Thanks again! I think writing some classes with methods will not be too difficult once the basic things about pitch notation and rhythmic notation are fixed.
Waiting for more opinions!